Korean Basic Grammar – ( 이다 )To be
Korean Basic Grammar – ( 이다 )To be
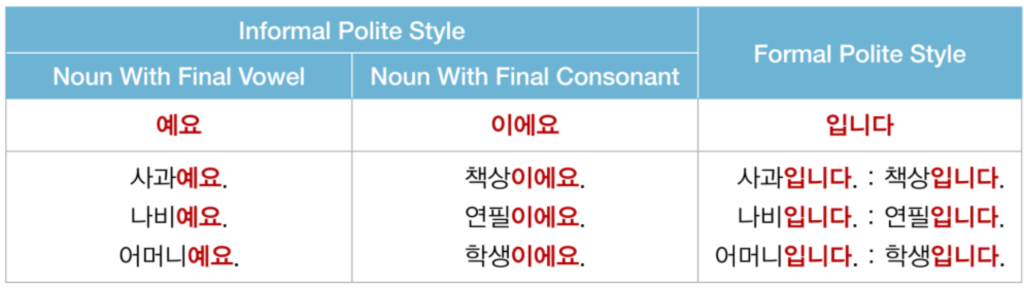
| ➤ 이다 attaches to the end of a noun to make it the predicate of the sentence. 이다 is used to express that the subject and predicate are the same thing. 이다 can also be used to specify something. ➤ The formal descriptive form is 입니다 and its interrogative form is 입니까? ➤The corresponding informal forms, 예요/이에요 are the same for both the descriptive and interrogative forms with the interrogative form rising in intonation as it is pronounced 예요?/이에요? When the preceding noun ends in a vowel 예요 is used and when the noun ends in a consonant 이에요 is used. ➤ The negative form of 이다 is 아니다. |

A: 무엇입니까? (→ 뭐예요?)
→ What’s this?
B: 의자입니다. (→ 의자예요.)
→ It’s a chair.

A: 한국 사람입니까? (→ 한국 사람이에요?)
→ Is She Korean?
B: 네, 한국 사람입니다. (→ 한국 사람이에요.)
→ Yes, She’s Korean.

A: 어디입니까? (→ 어디예요?)
→ What country is this?
B: 한국입니다. (→ 한국이에요.)
→ It’s Korea.
In Conversation
A: 무엇입니까? What is this?
B: 가방입니다. It’s a bag.
A:고향이 어디예요? Where is your hometown?
B: 서울이에요. Seoul.
A: 누구예요? Who is that?
B: 친구예요. That’s my friend.
A: 학생입니까? Are you a student?
B: 네, 학생입니다. Yes, I’m a student.
im so happy to learn this languge thx
I enjoy learning Korean language
hi
I’m so happy learn this language
Banglahash
Bajar
really really it’s so good amazing
good study
[email protected]
i want to learn Korea i really need this website
Good
Beatter
Superb
Hi sir,
Im srilankan can you put past and model paper question in english also after the test answer review mode because some times new words are there then its hard to understand the question while self study.
Just an concern 🙏🙏🙏